#SQL Server column existence
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Checking for the Existence of a Column in a SQL Server Table
To check if a column exists in a SQL Server table, you can use the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS system view, which provides information about all columns in all tables in a database. Here’s a SQL query that checks if a specific column exists in a specific table: IF EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE TABLE_NAME = 'YourTableName' AND COLUMN_NAME = 'YourColumnName' ) BEGIN PRINT…
View On WordPress
#check column SQL#INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS#SQL Server column existence#SQL Server table structure#validate SQL column
0 notes
Text
Structured Query Language (SQL): A Comprehensive Guide
Structured Query Language, popularly called SQL (reported "ess-que-ell" or sometimes "sequel"), is the same old language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. Developed in the early 1970s by using IBM researchers Donald D. Chamberlin and Raymond F. Boyce, SQL has when you consider that end up the dominant language for database structures round the world.
Structured query language commands with examples
Today, certainly every important relational database control system (RDBMS)—such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and SQLite—uses SQL as its core question language.
What is SQL?
SQL is a website-specific language used to:
Retrieve facts from a database.
Insert, replace, and delete statistics.
Create and modify database structures (tables, indexes, perspectives).
Manage get entry to permissions and security.
Perform data analytics and reporting.
In easy phrases, SQL permits customers to speak with databases to shop and retrieve structured information.
Key Characteristics of SQL
Declarative Language: SQL focuses on what to do, now not the way to do it. For instance, whilst you write SELECT * FROM users, you don’t need to inform SQL the way to fetch the facts—it figures that out.
Standardized: SQL has been standardized through agencies like ANSI and ISO, with maximum database structures enforcing the core language and including their very own extensions.
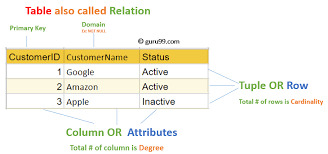
Relational Model-Based: SQL is designed to work with tables (also called members of the family) in which records is organized in rows and columns.
Core Components of SQL
SQL may be damaged down into numerous predominant categories of instructions, each with unique functions.
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL commands are used to outline or modify the shape of database gadgets like tables, schemas, indexes, and so forth.
Common DDL commands:
CREATE: To create a brand new table or database.
ALTER: To modify an present table (add or put off columns).
DROP: To delete a table or database.
TRUNCATE: To delete all rows from a table but preserve its shape.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE TABLE personnel (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
call VARCHAR(one hundred),
income DECIMAL(10,2)
);
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML commands are used for statistics operations which include inserting, updating, or deleting information.
Common DML commands:
SELECT: Retrieve data from one or more tables.
INSERT: Add new records.
UPDATE: Modify existing statistics.
DELETE: Remove information.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
INSERT INTO employees (id, name, earnings)
VALUES (1, 'Alice Johnson', 75000.00);
three. Data Query Language (DQL)
Some specialists separate SELECT from DML and treat it as its very own category: DQL.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT name, income FROM personnel WHERE profits > 60000;
This command retrieves names and salaries of employees earning more than 60,000.
4. Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL instructions cope with permissions and access manage.
Common DCL instructions:
GRANT: Give get right of entry to to users.
REVOKE: Remove access.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON personnel TO john_doe;
five. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
TCL commands manage transactions to ensure data integrity.
Common TCL instructions:
BEGIN: Start a transaction.
COMMIT: Save changes.
ROLLBACK: Undo changes.
SAVEPOINT: Set a savepoint inside a transaction.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
BEGIN;
UPDATE personnel SET earnings = income * 1.10;
COMMIT;
SQL Clauses and Syntax Elements
WHERE: Filters rows.
ORDER BY: Sorts effects.
GROUP BY: Groups rows sharing a assets.
HAVING: Filters companies.
JOIN: Combines rows from or greater tables.
Example with JOIN:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT personnel.Name, departments.Name
FROM personnel
JOIN departments ON personnel.Dept_id = departments.Identity;
Types of Joins in SQL
INNER JOIN: Returns statistics with matching values in each tables.
LEFT JOIN: Returns all statistics from the left table, and matched statistics from the right.
RIGHT JOIN: Opposite of LEFT JOIN.
FULL JOIN: Returns all records while there is a in shape in either desk.
SELF JOIN: Joins a table to itself.
Subqueries and Nested Queries
A subquery is a query inside any other query.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
SELECT name FROM employees
WHERE earnings > (SELECT AVG(earnings) FROM personnel);
This reveals employees who earn above common earnings.
Functions in SQL
SQL includes built-in features for acting calculations and formatting:
Aggregate Functions: SUM(), AVG(), COUNT(), MAX(), MIN()
String Functions: UPPER(), LOWER(), CONCAT()
Date Functions: NOW(), CURDATE(), DATEADD()
Conversion Functions: CAST(), CONVERT()
Indexes in SQL
An index is used to hurry up searches.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON employees(call);
Indexes help improve the performance of queries concerning massive information.
Views in SQL
A view is a digital desk created through a question.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
CREATE VIEW high_earners AS
SELECT call, salary FROM employees WHERE earnings > 80000;
Views are beneficial for:
Security (disguise positive columns)
Simplifying complex queries
Reusability
Normalization in SQL
Normalization is the system of organizing facts to reduce redundancy. It entails breaking a database into multiple related tables and defining overseas keys to link them.
1NF: No repeating groups.
2NF: No partial dependency.
3NF: No transitive dependency.
SQL in Real-World Applications
Web Development: Most web apps use SQL to manipulate customers, periods, orders, and content.
Data Analysis: SQL is extensively used in information analytics systems like Power BI, Tableau, and even Excel (thru Power Query).
Finance and Banking: SQL handles transaction logs, audit trails, and reporting systems.
Healthcare: Managing patient statistics, remedy records, and billing.
Retail: Inventory systems, sales analysis, and consumer statistics.
Government and Research: For storing and querying massive datasets.
Popular SQL Database Systems
MySQL: Open-supply and extensively used in internet apps.
PostgreSQL: Advanced capabilities and standards compliance.
Oracle DB: Commercial, especially scalable, agency-degree.
SQL Server: Microsoft’s relational database.
SQLite: Lightweight, file-based database used in cellular and desktop apps.
Limitations of SQL
SQL can be verbose and complicated for positive operations.
Not perfect for unstructured information (NoSQL databases like MongoDB are better acceptable).
Vendor-unique extensions can reduce portability.
Java Programming Language Tutorial
Dot Net Programming Language
C ++ Online Compliers
C Language Compliers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Optimizing Business Operations with Advanced Machine Learning Services
Machine learning has gained popularity in recent years thanks to the adoption of the technology. On the other hand, traditional machine learning necessitates managing data pipelines, robust server maintenance, and the creation of a model for machine learning from scratch, among other technical infrastructure management tasks. Many of these processes are automated by machine learning service which enables businesses to use a platform much more quickly.
What do you understand of Machine learning?
Deep learning and neural networks applied to data are examples of machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence focused on data-driven learning. It begins with a dataset and gains the ability to extract relevant data from it.
Machine learning technologies facilitate computer vision, speech recognition, face identification, predictive analytics, and more. They also make regression more accurate.
For what purpose is it used?
Many use cases, such as churn avoidance and support ticket categorization make use of MLaaS. The vital thing about MLaaS is it makes it possible to delegate machine learning's laborious tasks. This implies that you won't need to install software, configure servers, maintain infrastructure, and other related tasks. All you have to do is choose the column to be predicted, connect the pertinent training data, and let the software do its magic.
Natural Language Interpretation
By examining social media postings and the tone of consumer reviews, natural language processing aids businesses in better understanding their clientele. the ml services enable them to make more informed choices about selling their goods and services, including providing automated help or highlighting superior substitutes. Machine learning can categorize incoming customer inquiries into distinct groups, enabling businesses to allocate their resources and time.
Predicting
Another use of machine learning is forecasting, which allows businesses to project future occurrences based on existing data. For example, businesses that need to estimate the costs of their goods, services, or clients might utilize MLaaS for cost modelling.
Data Investigation
Investigating variables, examining correlations between variables, and displaying associations are all part of data exploration. Businesses may generate informed suggestions and contextualize vital data using machine learning.
Data Inconsistency
Another crucial component of machine learning is anomaly detection, which finds anomalous occurrences like fraud. This technology is especially helpful for businesses that lack the means or know-how to create their own systems for identifying anomalies.
Examining And Comprehending Datasets
Machine learning provides an alternative to manual dataset searching and comprehension by converting text searches into SQL queries using algorithms trained on millions of samples. Regression analysis use to determine the correlations between variables, such as those affecting sales and customer satisfaction from various product attributes or advertising channels.
Recognition Of Images
One area of machine learning that is very useful for mobile apps, security, and healthcare is image recognition. Businesses utilize recommendation engines to promote music or goods to consumers. While some companies have used picture recognition to create lucrative mobile applications.
Your understanding of AI will drastically shift. They used to believe that AI was only beyond the financial reach of large corporations. However, thanks to services anyone may now use this technology.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
DBMS Tutorial Explained: Concepts, Types, and Applications

In today’s digital world, data is everywhere — from social media posts and financial records to healthcare systems and e-commerce websites. But have you ever wondered how all that data is stored, organized, and managed? That’s where DBMS — or Database Management System — comes into play.
Whether you’re a student, software developer, aspiring data analyst, or just someone curious about how information is handled behind the scenes, this DBMS tutorial is your one-stop guide. We’ll explore the fundamental concepts, various types of DBMS, and real-world applications to help you understand how modern databases function.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software that enables users to store, retrieve, manipulate, and manage data efficiently. Think of it as an interface between the user and the database. Rather than interacting directly with raw data, users and applications communicate with the database through the DBMS.
For example, when you check your bank account balance through an app, it’s the DBMS that processes your request, fetches the relevant data, and sends it back to your screen — all in milliseconds.
Why Learn DBMS?
Understanding DBMS is crucial because:
It’s foundational to software development: Every application that deals with data — from mobile apps to enterprise systems — relies on some form of database.
It improves data accuracy and security: DBMS helps in organizing data logically while controlling access and maintaining integrity.
It’s highly relevant for careers in tech: Knowledge of DBMS is essential for roles in backend development, data analysis, database administration, and more.
Core Concepts of DBMS
Let’s break down some of the fundamental concepts that every beginner should understand when starting with DBMS.
1. Database
A database is an organized collection of related data. Instead of storing information in random files, a database stores data in structured formats like tables, making retrieval efficient and logical.
2. Data Models
Data models define how data is logically structured. The most common models include:
Hierarchical Model
Network Model
Relational Model
Object-Oriented Model
Among these, the Relational Model (used in systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle) is the most popular today.
3. Schemas and Tables
A schema defines the structure of a database — like a blueprint. It includes definitions of tables, columns, data types, and relationships between tables.
4. SQL (Structured Query Language)
SQL is the standard language used to communicate with relational DBMS. It allows users to perform operations like:
SELECT: Retrieve data
INSERT: Add new data
UPDATE: Modify existing data
DELETE: Remove data
5. Normalization
Normalization is the process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and improve integrity. It involves dividing a database into two or more related tables and defining relationships between them.
6. Transactions
A transaction is a sequence of operations performed as a single logical unit. Transactions in DBMS follow ACID properties — Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability — ensuring reliable data processing even during failures.
Types of DBMS
DBMS can be categorized into several types based on how data is stored and accessed:
1. Hierarchical DBMS
Organizes data in a tree-like structure.
Each parent can have multiple children, but each child has only one parent.
Example: IBM’s IMS.
2. Network DBMS
Data is represented as records connected through links.
More flexible than hierarchical model; a child can have multiple parents.
Example: Integrated Data Store (IDS).
3. Relational DBMS (RDBMS)
Data is stored in tables (relations) with rows and columns.
Uses SQL for data manipulation.
Most widely used type today.
Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server.
4. Object-Oriented DBMS (OODBMS)
Data is stored in the form of objects, similar to object-oriented programming.
Supports complex data types and relationships.
Example: db4o, ObjectDB.
5. NoSQL DBMS
Designed for handling unstructured or semi-structured data.
Ideal for big data applications.
Types include document, key-value, column-family, and graph databases.
Examples: MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, Neo4j.
Applications of DBMS
DBMS is used across nearly every industry. Here are some common applications:
1. Banking and Finance
Customer information, transaction records, and loan histories are stored and accessed through DBMS.
Ensures accuracy and fast processing.
2. Healthcare
Manages patient records, billing, prescriptions, and lab reports.
Enhances data privacy and improves coordination among departments.
3. E-commerce
Handles product catalogs, user accounts, order histories, and payment information.
Ensures real-time data updates and personalization.
4. Education
Maintains student information, attendance, grades, and scheduling.
Helps in online learning platforms and academic administration.
5. Telecommunications
Manages user profiles, billing systems, and call records.
Supports large-scale data processing and service reliability.
Final Thoughts
In this DBMS tutorial, we’ve broken down what a Database Management System is, why it’s important, and how it works. Understanding DBMS concepts like relational models, SQL, and normalization gives you the foundation to build and manage efficient, scalable databases.
As data continues to grow in volume and importance, the demand for professionals who understand database systems is also rising. Whether you're learning DBMS for academic purposes, career development, or project needs, mastering these fundamentals is the first step toward becoming data-savvy in today’s digital world.
Stay tuned for more tutorials, including hands-on SQL queries, advanced DBMS topics, and database design best practices!
0 notes
Text
SQL Database Fundamentals

SQL (Structured Query Language) is the standard language used to interact with relational databases. Whether you're building a small app or working on a large enterprise system, SQL is essential for storing, retrieving, and managing data effectively. This post introduces the key concepts and commands every beginner should know.
What is a Database?
A database is a structured collection of data that allows for easy access, management, and updating. SQL databases (like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite) organize data into tables that are related to each other.
What is SQL?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language. It is used to:
Create and manage databases
Insert, update, delete, and retrieve data
Control access and permissions
Basic SQL Commands
CREATE: Create a new database or table
INSERT: Add new data to a table
SELECT: Query and retrieve data
UPDATE: Modify existing data
DELETE: Remove data from a table
Example: Creating a Table
CREATE TABLE Users ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(100), email VARCHAR(100) );
Inserting Data
INSERT INTO Users (id, name, email) VALUES (1, 'Alice', '[email protected]');
Retrieving Data
SELECT * FROM Users;
Updating Data
UPDATE Users SET email = '[email protected]' WHERE id = 1;
Deleting Data
DELETE FROM Users WHERE id = 1;
Key Concepts to Learn
Tables and Rows: Tables store data in rows and columns.
Primary Keys: Unique identifier for each record.
Relationships: Data in one table can reference data in another.
Joins: Combine data from multiple tables.
Constraints: Rules for data integrity (e.g., NOT NULL, UNIQUE, FOREIGN KEY).
Common Types of SQL Databases
MySQL: Open-source and widely used for web development.
PostgreSQL: Advanced features and great performance.
SQLite: Lightweight, file-based database for small apps.
Microsoft SQL Server: Enterprise-grade database by Microsoft.
Helpful Resources
W3Schools SQL Tutorial
SQLZoo Interactive Learning
Codecademy Learn SQL
PostgreSQL Documentation
Conclusion
SQL is a foundational skill for anyone working with data or building applications. With just a few basic commands, you can begin managing and analyzing structured data effectively. Start practicing on a sample database and experiment with different queries — it’s the best way to learn!
0 notes
Text
Tips for Understanding Computer Databases for Homework Assignments

In today’s digital world, databases play a crucial role in managing and organizing vast amounts of information. Whether you're a student learning database concepts or working on complex assignments, understanding computer databases can be challenging. This blog will guide you through essential tips for mastering computer databases and help you complete your homework efficiently. If you're looking for computer database assistance for homework, All Assignment Experts is here to provide expert support.
What is a Computer Database?
A computer database is a structured collection of data that allows easy access, management, and updating. It is managed using a Database Management System (DBMS), which facilitates storage, retrieval, and manipulation of data. Popular database systems include MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Microsoft SQL Server.
Why is Understanding Databases Important for Students?
Databases are widely used in industries like banking, healthcare, and e-commerce. Students pursuing computer science, information technology, or data science must grasp database concepts to build a strong foundation for future careers. Database knowledge is essential for managing large data sets, developing applications, and performing data analysis.
Tips for Understanding Computer Databases for Homework Assignments
1. Master the Basics First
Before diving into complex queries, ensure you understand basic database concepts like:
Tables and Records: Databases store data in tables, which contain rows (records) and columns (fields).
Primary and Foreign Keys: Primary keys uniquely identify each record, while foreign keys establish relationships between tables.
Normalization: A technique to eliminate redundancy and improve database efficiency.
2. Learn SQL (Structured Query Language)
SQL is the standard language for managing databases. Some essential SQL commands you should learn include:
SELECT – Retrieve data from a database.
INSERT – Add new records to a table.
UPDATE – Modify existing records.
DELETE – Remove records from a table.
JOIN – Combine data from multiple tables.
Using online SQL playgrounds like SQL Fiddle or W3Schools can help you practice these commands effectively.
3. Use Online Resources and Tools
Numerous online platforms provide computer database assistance for homework. Websites like All Assignment Experts offer professional guidance, tutorials, and assignment help to enhance your understanding of databases. Other useful resources include:
W3Schools and TutorialsPoint for database tutorials.
YouTube channels offering step-by-step database lessons.
Interactive coding platforms like Codecademy.
4. Work on Real-Life Database Projects
Practical experience is the best way to solidify your knowledge. Try creating a small database for:
A library management system.
An online store with customer orders.
A student database with courses and grades.
This hands-on approach will help you understand real-world applications and make it easier to complete assignments.
5. Understand Database Relationships
One of the biggest challenges students face is understanding database relationships. The three main types include:
One-to-One: Each record in Table A has only one corresponding record in Table B.
One-to-Many: A record in Table A relates to multiple records in Table B.
Many-to-Many: Multiple records in Table A relate to multiple records in Table B.
Using Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) can help visualize these relationships.
6. Debug SQL Queries Effectively
If your SQL queries aren’t working as expected, try these debugging techniques:
Break queries into smaller parts and test them individually.
Use EXPLAIN to analyze how queries are executed.
Check for syntax errors and missing table relationships.
7. Seek Expert Assistance When Needed
If you find yourself struggling, don’t hesitate to seek help. All Assignment Experts offers computer database assistance for homework, providing expert solutions to your database-related queries and assignments.
8. Stay Updated with Advanced Database Technologies
The database field is constantly evolving. Explore advanced topics such as:
NoSQL Databases (MongoDB, Firebase): Used for handling unstructured data.
Big Data and Cloud Databases: Learn about databases like AWS RDS and Google BigQuery.
Data Security and Encryption: Understand how databases protect sensitive information.
Conclusion
Understanding computer databases is crucial for students handling homework assignments. By mastering basic concepts, practicing SQL, utilizing online resources, and working on real projects, you can excel in your database coursework. If you need professional guidance, All Assignment Experts provides top-notch computer database assistance for homework, ensuring you grasp key concepts and score better grades.
Start applying these tips today, and you’ll soon develop a solid understanding of databases!
#computer database assistance for homework#computer database assistance#education#homework#do your homework
1 note
·
View note
Text
MySQL Naming Conventions

What is MySQL?
MySQL is a freely available open source Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) that uses Structured Query Language (SQL). SQL is the most popular language for adding, accessing and managing content in a database. It is most noted for its quick processing, proven reliability, ease and flexibility of use.
What is a naming convention?
In computer programming, a naming convention is a set of rules for choosing the character sequence to be used for identifiers that denote variables, types, functions, and other entities in source code and documentation.
General rules — Naming conventions
Using lowercase will help speed typing, avoid mistakes as MYSQL is case sensitive.
Space replaced with Underscore — Using space between words is not advised.
Numbers are not for names — While naming, it is essential that it contains only Alpha English alphabets.
Valid Names — Names should be descriptive of the elements. i.e. — Self-explanatory and not more than 64 characters.
No prefixes allowed.
Database name convention
Name can be singular or plural but as the database represents a single database it should be singular.
Avoid prefix if possible.
MySQL table name
Lowercase table name
MySQL is usually hosted in a Linux server which is case-sensitive hence to stay on the safe side use lowercase. Many PHP or similar programming frameworks, auto-detect or auto-generate class-based table names and most of them expect lowercase names.
Table name in singular
The table is made up of fields and rows filled with various forms of data, similarly the table name could be plural but the table itself is a single entity hence it is odd and confusing. Hence use names like User, Comment.
Prefixed table name
The table usually has the database or project name. sometimes some tables may exist under the same name in the database to avoid replacing this, you can use prefixes. Essentially, names should be meaningful and self-explanatory. If you can’t avoid prefix you can fix it using php class.
Field names
Use all above cases which include lowercase, no space, no numbers, and avoid prefix.
Choose short names no-longer than two words.
Field names should be easy and understandable
Primary key can be id or table name_id or it can be a self-explanatory name.
Avoid using reserve words as field name. i.e. — Pre-defined words or Keywords. You can add prefix to these names to make it understandable like user_name, signup_date.
Avoid using column with same name as table name. This can cause confusion while writing query.
Avoid abbreviated, concatenated, or acronym-based names.
Do define a foreign key on database schema.
Foreign key column must have a table name with their primary key.
e.g. blog_id represents foreign key id from table blog.
Avoid semantically — meaningful primary key names. A classic design mistake is creating a table with primary key that has actual meaning like ‘name’ as primary key. In this case if someone changes their name then the relationship with the other tables will be affected and the name can be repetitive losing its uniqueness.
Conclusion
Make your table and database names simple yet understandable by both database designers and programmers. It should things that might cause confusion, issues with linking tables to one another. And finally, it should be readable for programming language or the framework that is implemented.
#MySQL#DatabaseManagement#SQL#NamingConventions#RelationalDatabase#DatabaseDesign#CodingStandards#TableNaming#FieldNaming#DatabaseSchema#ProgrammingTips#DataManagement#CaseSensitivity#PrimaryKey#ForeignKey#DatabaseBestPractices#OpenSource#DatabaseOptimization#MySQLTips#DataStructure
0 notes
Text
Cómo instalar PostgreSQL en Windows paso a paso

PostgreSQL es un sistema de bases de datos relacional y de código abierto ampliamente utilizado por su robustez y soporte para funciones avanzadas como JSON y operaciones geoespaciales. A continuación, te mostramos cómo instalar PostgreSQL en Windows y realizaremos una práctica personalizada para confirmar que los alumnos completaron la instalación y el uso del sistema. Requisitos previos - Sistema operativo: Windows 10 o superior. - Memoria RAM mínima: 4 GB. - Espacio libre en disco: Al menos 2 GB. - Conexión a internet para descargar el instalador. Para este tema, es importante tomar capturas de pantalla de todo el proceso, para que entregues las evidencias de lo realizado. Paso a paso para instalar PostgreSQL Paso 1: Descargar el instalador - Ve al sitio oficial de PostgreSQL: Descargar PostgreSQL. - Selecciona Windows y haz clic en el enlace para descargar el instalador correspondiente.


Paso 2: Ejecutar el instalador - Una vez descargado, haz doble clic en el archivo postgresql-17.0-1-windows.exe - En la primera pantalla, haz clic en Next.

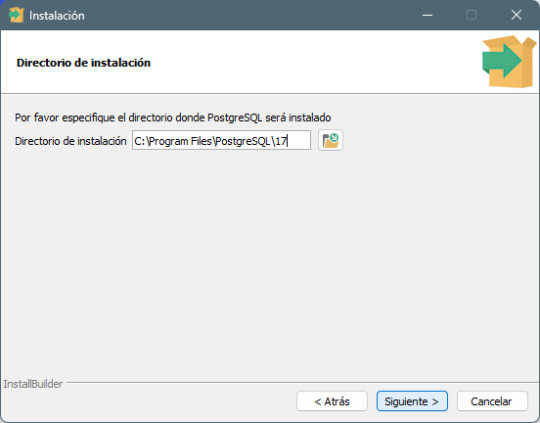
Paso 3: Selección del directorio de instalación - Elige la carpeta donde deseas instalar PostgreSQL o deja la predeterminada. - Haz clic en Next.
Paso 4: Selección de componentes - Asegúrate de seleccionar: - PostgreSQL Server - pgAdmin 4 (herramienta gráfica para administrar bases de datos) - Haz clic en Next.

Paso 5: Configuración de la contraseña del superusuario - Introduce y confirma una contraseña para el usuario postgres (anótala, la necesitarás más adelante). - Haz clic en Next.

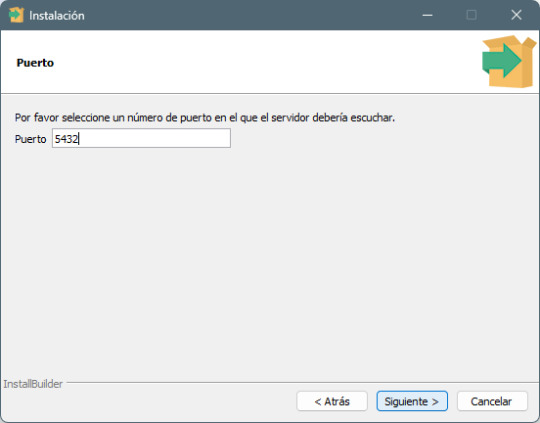
Paso 6: Configuración del puerto de conexión - Deja el puerto predeterminado 5432 (a menos que necesites cambiarlo por alguna razón). - Haz clic en Next.

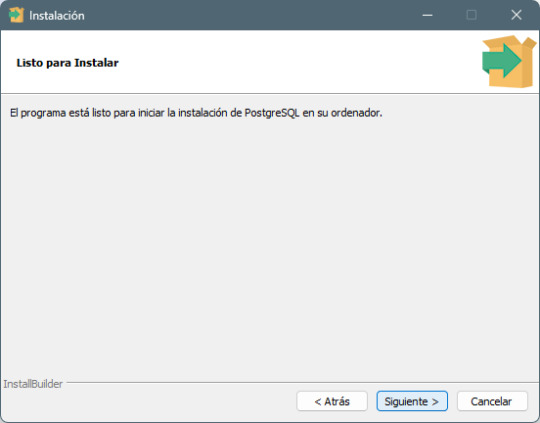
Paso 7: Finalización de la instalación - Haz clic en Next y luego en Finish para completar la instalación. - PostgreSQL y pgAdmin 4 estarán ahora listos para ser usados.
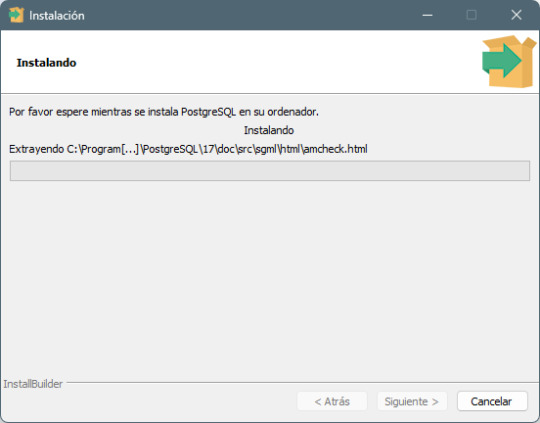
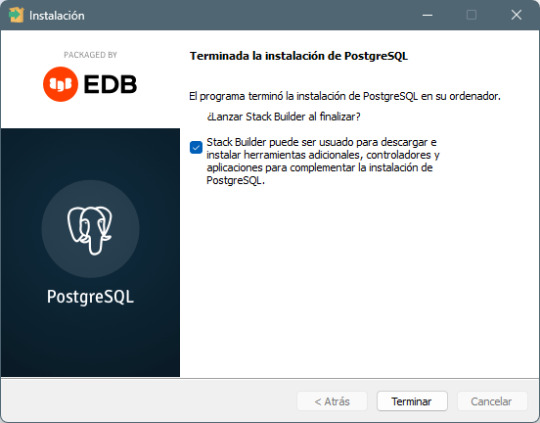
Paso a paso para usar PostgreSQL con pgAdmin 4

Paso 1: Abrir pgAdmin 4

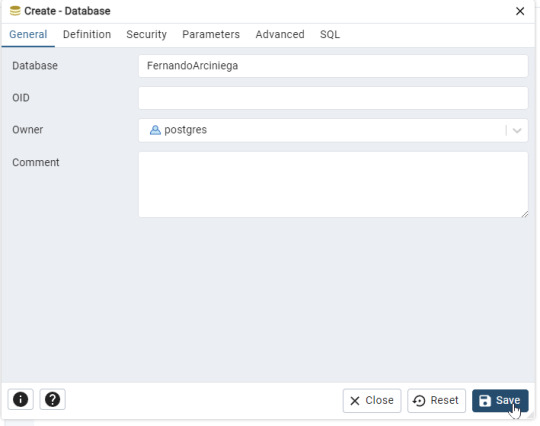
- Desde el menú de inicio, abre pgAdmin 4. - Ingresa la contraseña que configuraste para el usuario postgres. Paso 2: Crear una nueva base de datos - En el panel izquierdo, haz clic derecho sobre Databases y selecciona Create > Database.

- En el campo Database Name, ingresa tu nombre y tu primer apellido (por ejemplo: FernandoArciniega). - Haz clic en Save para crear la base de datos.
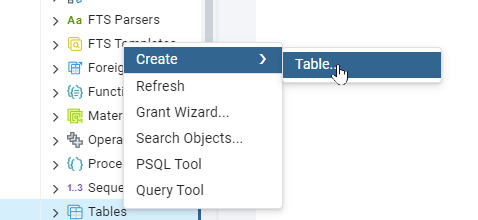
Paso 3: Crear una tabla personalizada - Selecciona tu base de datos y ve a Schemas > Tables.

- Haz clic derecho en Tables y selecciona Create > Table.
- Asigna un nombre a la tabla, como Estudiantes_ (por ejemplo: Estudiantes_FOAM).
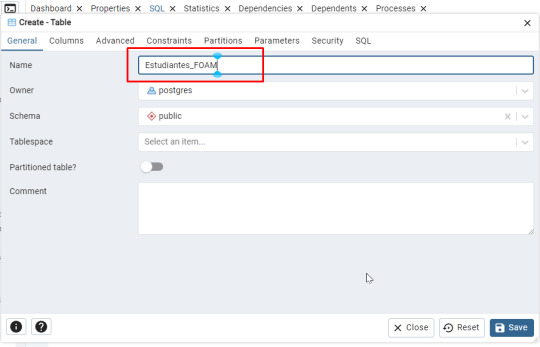
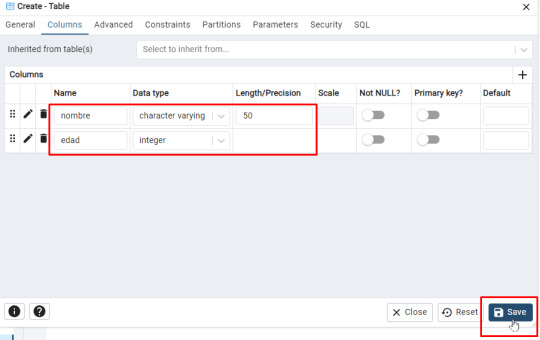
Agrega dos columnas: (Ficha Columns)

- Nombre (Tipo: character varying(50)) - Edad (Tipo: integer)
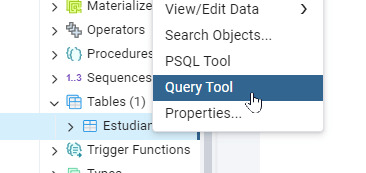
- Guarda la tabla haciendo clic en Save. Aparecerá el siguiente código: -- Table: public.Estudiantes_FOAM -- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS public."Estudiantes_FOAM"; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public."Estudiantes_FOAM" ( nombre character varying(50) COLLATE pg_catalog."default", edad integer ) TABLESPACE pg_default; ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS public."Estudiantes_FOAM" OWNER to postgres; Paso 4: Insertar datos en la tabla - Haz clic derecho en la tabla y selecciona Query Tool.
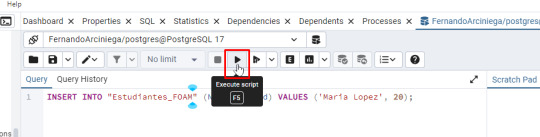
- Escribe la siguiente consulta SQL para insertar un registro: INSERT INTO "Estudiantes_FOAM" (Nombre, Edad) VALUES ('Maria Lopez', 20); - Haz clic en Run para ejecutar la consulta o F5
Paso 5: Verificar los datos - Haz clic derecho en la tabla y selecciona View/Edit Data > All Rows. - Verifica que el registro se haya insertado correctamente.

Inserta 14 registroas más para tener un total de 15 en tu tabla. Práctica: Demostrar la instalación y uso de PostgreSQL Instrucciones personalizadas para la entrega: - Base de datos personalizada: - Cada alumno debe crear una base de datos con su nombre completo. - Tabla personalizada: - Crear una tabla con el nombre Estudiantes_ (por ejemplo: Estudiantes_FOAM). - Inserción de registro: - Inserta 15 registros en total con su nombre y edad. Entrega del trabajo - Formato: Impreso. - Equipos de 4 personas. Read the full article
#basededatosgratuita#basededatosrelacionalWindows#basesdedatosparaprincipiantes#cómousarpgAdmin#conexiónaPostgreSQL#configuraciónPostgreSQL#crearbasededatosenPostgreSQL#crearbasededatospersonalizada#creartablaenPostgreSQL#descargarPostgreSQLgratis#insertardatosPostgreSQL#instalacióndePostgreSQL2024#instalaciónfácilPostgreSQL#instalarpgAdmin4#PostgreSQLejercicios#PostgreSQLinstalaciónWindows#PostgreSQLManagementTool#PostgreSQLparaestudiantes#PostgreSQLpasoapaso#prácticasconPostgreSQL#servidorPostgreSQLlocal#SQLenPostgreSQL#tutorialpgAdminpasoapaso#tutorialPostgreSQLenespañol
0 notes
Text
Analysing large data sets using AWS Athena
Handling large datasets can feel overwhelming, especially when you're faced with endless rows of data and complex information. At our company, we faced these challenges head-on until we discovered AWS Athena. Athena transformed the way we handle massive datasets by simplifying the querying process without the hassle of managing servers or dealing with complex infrastructure. In this article, I’ll Walk you through how AWS Athena has revolutionized our approach to data analysis. We’ll explore how it leverages SQL to make working with big data straightforward and efficient. If you’ve ever struggled with managing large datasets and are looking for a practical solution, you’re in the right place.
Efficient Data Storage and Querying
Through our experiences, we found that two key strategies significantly enhanced our performance with Athena: partitioning data and using columnar storage formats like Parquet. These methods have dramatically reduced our query times and improved our data analysis efficiency. Here’s a closer look at how we’ve implemented these strategies:
Data Organization for Partitioning and Parquet
Organize your data in S3 for efficient querying:
s3://your-bucket/your-data/
├── year=2023/
│ ├── month=01/
│ │ ├── day=01/
│ │ │ └── data-file
│ │ └── day=02/
│ └── month=02/
└── year=2024/
└── month=01/
└── day=01/
Preprocessing Data for Optimal Performance
Before importing datasets into AWS Glue and Athena, preprocessing is essential to ensure consistency and efficiency. This involves handling mixed data types, adding date columns for partitioning, and converting files to a format suitable for Athena.
Note: The following steps are optional based on the data and requirements. Use them according to your requirements.
1. Handling Mixed Data Types
To address columns with mixed data types, standardize them to the most common type using the following code snippet:def determine_majority_type(series): # get the types of all non-null values types = series.dropna().apply(type) # count the occurrences of each type type_counts = types.value_counts()
preprocess.py
2. Adding Date Columns for Partitioning
To facilitate partitioning, add additional columns for year, month, and day:def add_date_columns_to_csv(file_path): try: # read the CSV file df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
partitioning.py
3. Converting CSV to Parquet Format
For optimized storage and querying, convert CSV files to Parquet format:def detect_and_convert_mixed_types(df): for col in df.columns: # detect mixed types in the column if df[col].apply(type).nunique() > 1:
paraquet.py
4. Concatenating Multiple CSV Files
To consolidate multiple CSV files into one for Parquet conversion:def read_and_concatenate_csv_files(directory): all_dfs = [] # recursively search for CSV files in the directory
concatenate.py
Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Datasets with AWS Glue and Athena
1. Place Your Source Dataset in S3
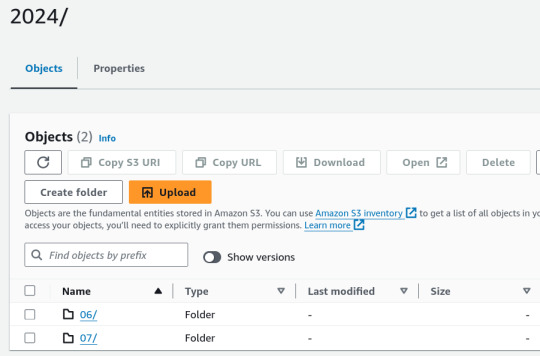
2. Create a Crawler in AWS Glue
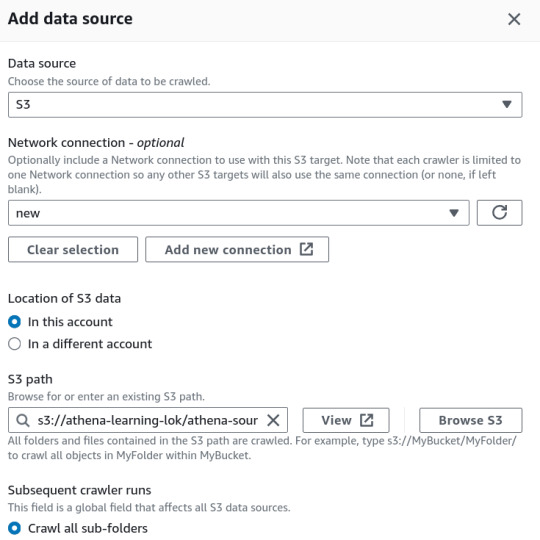
In the AWS Glue console, create a new crawler to catalog your data and make it queryable with Athena.
Specify Your S3 Bucket: Set the S3 bucket path as the data source in the crawler configuration.
IAM Role: Assign an IAM role with the necessary permissions to access your S3 bucket and Glue Data Catalog.
3. Set Up the Glue Database
Create a new database in the AWS Glue Data Catalog where your CSV data will be stored. This database acts as a container for your tables.
Database Creation: Go to the AWS Glue Data Catalog section and create a new database.
Crawler Output Configuration: Specify this database for storing the table metadata and optionally provide a prefix for your table names.
4. Configure Crawler Schedule
Set the crawler schedule to keep your data catalog up to date:
Hourly
Daily
Weekly
Monthly
On-Demand
Scheduling the crawler ensures data will be updated to our table, if any updates to existing data or adding of new files etc.
5. Run the Crawler
Initiate the crawler by clicking the "Run Crawler" button in the Glue console. The crawler will analyze your data, determine optimal data types for each column, and create a table in the Glue Data Catalog.
6. Review and Edit the Table Schema
Post-crawler, review and modify the table schema:
Change Data Types: Adjust data types for any column as needed.
Create Partitions: Set up partitions to improve query performance and data organization.

7. Query Your Data with AWS Athena
In the Athena console:
Connect to Glue Database: Use the database created by the Glue Crawler.
Write SQL Queries: Leverage SQL for querying your data directly in Athena.
8. Performance Comparison
After the performance optimizations, we got the following results:
To illustrate it, I ran following queries on 1.6 GB data:
For Parquet data format without partitioning
SELECT * FROM "athena-learn"."parquet" WHERE transdate='2024-07-05';
For Partitioning with CSV

Query Runtime for Parquet Files: 8.748 seconds. Parquet’s columnar storage format and compression contribute to this efficiency.
Query Runtime for Partitioned CSV Files: 2.901 seconds. Partitioning helps reduce the data scanned, improving query speed.
Data Scanned for Paraquet Files: 60.44MB
Data Scanned for Partitioned CSV Files: 40.04MB
Key Insight: Partitioning CSV files improves query performance, but using Parquet files offers superior results due to their optimized storage and compression features.
9. AWS Athena Pricing and Optimization
AWS Athena pricing is straightforward: you pay $5.00 per terabyte (TB) of data scanned by your SQL queries. However, you can significantly reduce costs and enhance query performance by implementing several optimization strategies.
Conclusion
AWS Athena offers a powerful, serverless SQL interface for querying large datasets. By adopting best practices in data preprocessing, organization, and Athena usage, you can manage and analyze your data efficiently without the overhead of complex infrastructure.
0 notes
Link
SQL Server: How to Use the ADD Keyword for Schema Changes
When working with SQL Server, managing and modifying database schemas is a fundamental task. One of the key operations you might frequently perform is adding new columns, constraints, or indexes to your existing tables. This is where the ADD keyword becomes incredibly useful. This blog post will delve into how to effectively use the ADD keyword in SQL Server to perform schema changes, complete with code examples to illustrate each scenario...
Learn more here:
https://www.nilebits.com/blog/2024/07/sql-server-add-keyword-for-schema-changes/
0 notes
Text
SQL and NoSQL: Differences, Use cases and Databases
SQL and NoSQL are counter technologies meant to accomplish the same business goals. The difference mainly exists in the autonomy to ‘explore data deeply’ and ‘ease of scalability’
SQL has existed as a widely accepted industry standard for so long now. Its counterpart; NoSQL, emerged almost 12 years ago when the world needed a disparate system that could process unstructured data as well as comply with increasing storage and power requirements.
The rise of NoSQL almost diminished the decade old SQL paradigm of relational database management system (RDBMS) giving rise to non relational database systems.
Now as we see, SQL didn’t go away, instead its potential to manipulate data in databases is increasingly realized.
In this article, we explore sql and nosql difference, sql vs. nosql use cases, and comparison of databases.
SQL and NoSQL Difference
The differences in SQL and NoSQL exist among four key parameters: Language, Scalability, Structure, and Transaction Processing.
Language
SQL is used to query structured data only. Structured data exists in the form of rows and columns (2D tables) and therefore exert the constraint for a carefully built schema before querying data.
That’s because for data whose structure could not be defined; data from mobile applications, and SAP systems with a lot of varying fields where new fields occur every now and then, SQL fails given its syntax and control flow that works only for table based data.
Apart from the structure constraint on data, SQL has been well nurtured in the past 40 years to offer wide functionality for complex queries, and is secure in usage.
The learning curve of SQL is also short compared to other programming languages (including NoSQL). Moreover, all the variants of SQL including for example SQL server, and MySQL have a great amount of similarity in usage and therefore are easily learnt across the globe.
NoSQL has its own advantages over SQL. It offers the flexibility to query unstructured data (with a dynamic schema not limited to representing data in rows and columns). This means now each type of data could have alternate structure all stored beside each other in a single database.
NoSQL was introduced some 12 years ago with the aim of utilization of unstructured or loosely structured data in database applications.
There’s freedom from rigorous data engineering before the storage to use the data for BI and ML applications. NoSQL offers greater exploration of data in that the raw data is directly fed to the system for storage and after that the BI and ML engineers could build schemas as they like.
The spotlight on NoSQL waned when its users realized it lacked standardization and wide documentation leading to difficulty in carrying out complex queries.
Moreover, NoSQL language varies across databases where each database (MongoDB, Cassandra, etc) have their completely varying versions of noSQL.CategorySQLNoSQLLanguageStructured data onlyStructured and unstructuredScalabilityVerticalHorizontalStructureTable format4 Types incl. columnar formatTransactionsACID complianceCAP theoremSQL vs. NoSQL Difference
Scalability
Scalability is one of the most distinctive features of SQL and NoSQL databases. For the scope of this article, we define scalability as the capacity of a system to process a number of concurrent queries.
The ease of adding and removing processing resources for the purpose of supporting concurrent users determines the effectiveness of scalability.
SQL supports vertical scalability that means new processing resources could be added within the same server. It’s based on the actor model that uses multiple CPU cores. All the processor cores participate in processing over the same data.
NoSQL adopts the horizontal scalability that instead of adding cores to CPU adds new servers in parallel to old ones. It uses a master/slave architecture where a master processor divides data among slave processors.
In essence, horizontal scaling is more desirable due to its ability to divide data across parallel machines. This way it enables faster processing from utilization of all resources in less time. Whereas vertical scaling, although much easier to implement, lacks the kind of linear scalability as in horizontal scaling.
Learn more about differences in horizontal scalability and vertical scalability here.
Structure
SQL databases store data in rows and columns where a column represents a specific data type only. While making these tables some rules are defined to maintain the integrity of data as well as making it efficient for the querying process.
NoSQL databases don’t conform to this tabular structure, and don’t require data engineering such as above. Instead they use other formats that are more flexible to add any kind of data desired. These formats are:
Column-oriented structure: Data resides in columns however these columns support any kind of data type. It results in high dimensional data.
Key-Value structure: Data objects are defined and a unique key is assigned to each object.
Document stores: specifically holds semi-structured data where some of the data is structured, while it may contain other data that has no defined column category.
Graph databases: It uses nodes and relationships to structure data instead of a table or a document. Nodes present data elements while relationships present how they are related to each other.
Learn more about Graph databases in this comprehensive article.
Transaction Processing
As you may be well aware that SQL databases process transactions in such a way as to minimize the erroneous events that might affect the data. For this, it uses the ACID rules. These are the:
Atomicity of a transaction prevents it from getting saved when it’s incomplete. A transaction is either saved when it’s completed only or failed otherwise.
Consistency prevents data from being corrupted by following rules at each step of transactional processing.
Isolation keeps away multiple users to change the same data at same time.
Durability records a transaction once it is made. No roll back can be done after a transaction is saved.
In distributed systems as a copy of data is stored on all distributed nodes through replication the transactional processing is a little different. NoSQL uses the CAP theorem that is specifically designed for successful transaction processing on distributed systems.
Consistency ensures the delivery of latest results where sometimes in case of a node separated from the system due to a network failure might not receive the updated information. An error message must be sent to the user instead of an unlatest value fetched from a node.
Availability, unlike a consistent system, ensures that a transaction is always successful (returning a non-error result) even when there’s network failure.
Partition Tolerance is a phenomenon for uninterruptible system performance in case of a network failure between parallel systems. More than one link is created among nodes such that if a link fails, there are other links that duplicate data to other nodes.
In NoSQL databases, only two properties are fulfilled at a time, that is, either CA, CP, or AP.
Learn more about the CAP theorem with example cases in this insightful article.
SQL vs NoSQL Use Cases
SQL databases are preferred when scalability requirements are not very large. This simply means it won’t support concurrent requests from a large number of users such as those in big data applications.
Big data applications demand storage of huge sized and highly varied data that arrives very frequently on databases. These applications require processing of both structured and unstructured data as well as require high scalability needs.
For big data applications, NoSQL databases have immense use cases and are preferred over SQL based solutions.
Quite surprisingly, today we see some unique database solutions that leverage the SQL language to query ‘big data’ stored across the distributed systems in the cloud. Examples include Snowflake’s relational database that is scalable as well as capable of storing semi-structured data.
Learn more about Snowflake’s unique approach in this comprehensive article.
Databases
Today the old SQL based databases have started to invent NoSQL like features to compete against the rising technology.
We call it ‘Combined Strength’ that uses the good points of both technologies to enable rich and more flexible database experience.
Today MySQL of Oracle has evolved to support semi-structured data such as JSON and document based files along with support for horizontal scaling
Meanwhile, on the non-relational end, NoSQL databases such as MongoDB also offer relational features such as indexing, aggregation queries, and ACID compliance in its document based data format.
Moreover, the noSQL databases have increasingly adopted a SQL-based syntax for attracting data analysts and data scientists who have extensive SQL experience and limited programing knowhow.
Adding to that, Cassandra has CQL, Spark developed SparkQL, and JIRA developed JQL.
Although the NoSQL databases have a lot to offer through its support for programming languages, building a SQL-like support can empower those with SQL know-how to use the best of their knowledge.
Conclusion
The SQL vs. NoSQL debate has evolved from a clear-cut dichotomy to a more nuanced understanding of their strengths and weaknesses. Modern databases often blend elements of both approaches, offering flexibility and scalability.
Dicecamp's Data Engineering Course Using SQL Server Tools could be a valuable resource for individuals looking to master SQL and its applications in the modern data landscape. By focusing on SQL Server tools, the course likely equips students with practical skills to work with relational databases and potentially explore their integration with NoSQL technologies.
Would you like to learn more about specific SQL Server tools or how they can be used in conjunction with NoSQL databases.
0 notes
Text
Setting References, Adding constraints
We need to set up some items so that eventually this project will actually run. First off, we need to set up a reference to an existing server where the project will be exported when we're finished.
Under the Solution's name, there is a entry for References. Right-click on that, then select Database References. Change the database reference type to System Database, and select the master database.
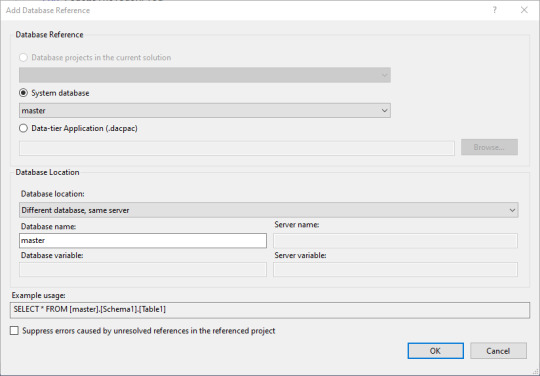
Just to be fair, I had trouble with adding the default as below. I kept getting an error SLQ17501, meaning the editor was unable to find the referred to item.
There is an equivalent of SSMS' Crtl+Shift+R, which in the Project menu then Reanalyze Project. And that didn't work. It's supposed to take a little bit like the refresh of the table data into IntelliSense does in SSMS, so I waited. Hours.
Then I deleted the offending item and tried to add it again. Still there.
Then deleted the entire project and started over. At that point, in the error listing, I noticed the project was set for "Build + Intellisense". Clicking the other options confirmed that the problem was in IntelliSense, not the Build.
Next day, I started off with a new and smaller build and planned on using VS to report the issue to Microsoft. And it never came back. Anywhere. Computer Science is in the next classroom, this is working with software, which is a whole different beast. End interruption.
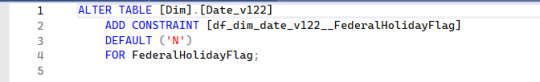
The source table has the one constraint already, which is the clustered primary key. "Clustered" means that the data will be put in the specified order onto the drive. Primary keys have to be non-null and unique, and are often what is used as a foreign key in another table.
This is a table of dates, and there's already date functions and tools built in to SQL. Why add more? Mostly so that we have a simple table to join on for long calculations. You can figure out if a given day is a weekend by looking at the DatePart() function with the first parameter set to DW. But is it a holiday? That is a bit harder to work out. This table does the calculations so they don't have to be repeated endlessly.
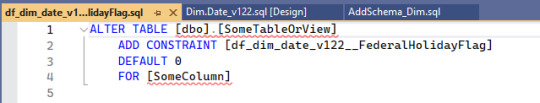
First off, let's set the FederalHolidayFlag to default to the character 'N'. We do the right-click on the solution's name, then Add, then New Item. Under Tables and Views we can select a Default Constraint. And it wants a name again.
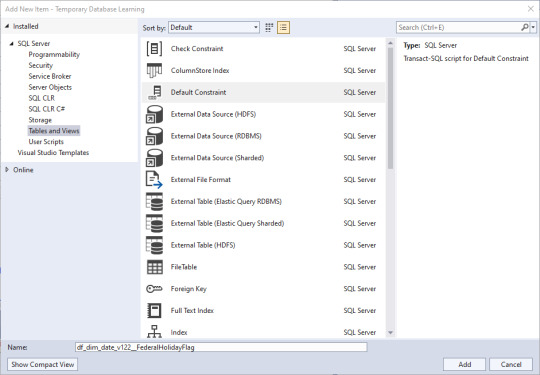
And VS is helping where it can.
There's a related Check Constraint. Everybody is going to have opinions about where each of the files should be one single step, or if all the related steps should stay together. Make a choice that appeals to you, and realize unless you're the project manager it doesn't matter. I want the practice using the different templates.
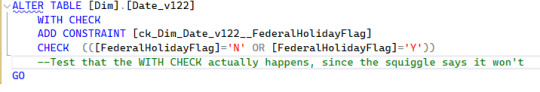
The blue squiggle is error SQL70588 - since there's already a data enforcement check on that column, the WITH CHECK part of the statement will be ignored. I'm making a note that the Test Suite needs to look at that.
Document it. Always. Or you will forget.
Why use 'Y' and 'N'? One byte is the smallest column size. The boolean columns do only take up one bit in some byte, but unless you have a lot of booleans (8 or more), it's not much of a savings in space and a tad more work in CPU - probably breaks even in the long run. We could have used 0 and 1 in a tinyint column. It was an aesthetic choice on the part of the Data Architect team.
There are a bunch more constraints we could put in. Which ones matter to you?
0 notes
Text
Exploring Tableau: Beginner-Friendly Tutorial
Are you ready to dive into the fascinating world of data visualization with Tableau? Whether you're a data enthusiast, a student, or a professional looking to enhance your analytical skills, Tableau offers a user-friendly platform to create stunning visualizations and gain valuable insights from your data. In this beginner-friendly tutorial, we'll walk through the basics of Tableau, step by step, so you can start harnessing its power with confidence.
1. Introduction to Tableau
Let's start with the basics. Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive and shareable dashboards, reports, and charts. It's widely used across various industries for data analysis, business intelligence, and decision-making.
2. Getting Started with Tableau
To begin your Tableau journey, you'll need to download and install Tableau Desktop, the main application for creating visualizations. Once installed, launch Tableau Desktop and you're ready to go.
3. Connecting to Data Sources
Tableau allows you to connect to a wide range of data sources including Excel files, databases like SQL Server and MySQL, cloud platforms like Google BigQuery, and more. To import your data into Tableau, simply click on the "Connect" option and choose your desired data source.
4. Understanding Tableau Workspace
Tableau's workspace consists of various components such as data pane, shelves, cards, and toolbar. The data pane displays the data tables and fields from your connected data source, while shelves are used to build visualizations by dragging and dropping fields onto rows, columns, or marks cards.
5. Creating Basic Visualizations
Now it's time to create your first visualization in Tableau. Start by dragging a field from the data pane onto the rows or columns shelf to create a basic chart such as a bar chart or line graph. You can further customize your visualization by adding filters, sorting data, and formatting the appearance.
6. Building Interactive Dashboards
One of Tableau's standout features is its ability to create interactive dashboards that allow users to explore data dynamically. To build a dashboard, simply drag visualizations onto the dashboard canvas and arrange them as desired. You can then add interactivity by creating filters, parameters, and actions.
7. Using Calculated Fields and Parameters
Tableau offers advanced functionality through calculated fields and parameters, allowing users to perform calculations and create dynamic controls within their visualizations. Calculated fields enable you to create new fields based on existing data, while parameters allow users to input values dynamically and control aspects of the visualization.
8. Exploring Advanced Visualization Techniques
As you become more comfortable with Tableau, you can explore advanced visualization techniques to create more complex and insightful visualizations. This includes techniques such as dual-axis charts, trend lines, geographic maps, and advanced analytics using Tableau's built-in functions and features.
9. Sharing and Collaborating
Once you've created your visualizations and dashboards, it's time to share your insights with others. Tableau offers various options for sharing and collaborating including publishing to Tableau Server or Tableau Online, embedding visualizations in websites or presentations, and exporting as image or PDF files.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You've completed our beginner-friendly Tableau tutorial and are now equipped with the basic knowledge to start exploring and creating visualizations with Tableau. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don't hesitate to experiment with different features and techniques to unleash the full potential of Tableau for your data analysis needs. Happy visualizing!
0 notes
Text
Azure Data Engineer Course | Azure Data Engineer Online Training
Architecture And Usage Of Different Azure Services
Azure Microsoft cloud computing platform, offers a wide range of services to help organizations build, deploy, and manage various applications and solutions. Here's an overview of some key Azure services along with their architecture and common usage
Azure Data Engineer Training Ameerpet

Azure Virtual Machines (VMs):
Architecture: Azure VMs provide on-demand computing resources with customizable configurations, including CPU, memory, and storage. They run on Microsoft's Hyper-V hypervisor technology.
Usage: Ideal for migrating existing applications to the cloud, hosting websites, running development and test environments, and deploying enterprise applications. - Azure Data Engineer Online Training
Azure App Service:
Architecture: A fully managed platform for building, deploying, and scaling web apps, mobile backends, and APIs. It supports multiple programming languages and frameworks.
Usage: Hosting web applications, APIs, mobile app backends, and RESTful services. It's popular for building and deploying web applications quickly without managing infrastructure.
Azure Functions:
Architecture: A serverless compute service that allows you to run event-triggered code without managing infrastructure. It automatically scales based on demand. - Azure Data Engineer Training
Usage: Implementing microservices, event-driven applications, serverless workflows, and automation tasks.
Azure SQL Database:
Architecture: A fully managed relational database service based on Microsoft SQL Server. It offers high availability, security, and automated backups.
Usage: Storing and managing relational data, supporting OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) workloads, and building line-of-business applications.
Azure Cosmos DB:
Architecture: A globally distributed, multi-model database service designed for building highly responsive and scalable applications. It supports multiple data models, including document, key-value, graph, and column family.
Usage: Building real-time applications, IoT solutions, gaming leaderboards, and globally distributed applications that require low-latency access to data.
- Data Engineer Course in Hyderabad
Azure Blob Storage:
Architecture: A scalable object storage service for storing large amounts of unstructured data, such as images, videos, documents, and backups.
Usage: Storing files for web applications, archiving data, serving static website content, and storing data for analytics.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS):
Architecture: A managed Kubernetes service for deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications using Kubernetes.
Usage: Orchestrating containerized workloads, deploying microservices architecture, and building cloud-native applications.
- Azure Data Engineer Training Hyderabad
Azure Active Directory (AAD):
Architecture: A cloud-based identity and access management service that provides authentication and authorization services for applications.
Usage: Securing access to applications, managing user identities, implementing single sign-on (SSO), and integrating with other Azure services.
These are just a few examples of the many services offered by Azure, each designed to address specific use cases and requirements of modern applications and solutions.
Visualpath is the Best Software Online Training Institute in Hyderabad. Avail complete Azure Data Engineer Training worldwide. You will get the best course at an affordable cost.
Attend Free Demo
Call on - +91-9989971070.
WhatsApp: https://www.whatsapp.com/catalog/919989971070
Visit https://visualpath.in/azure-data-engineer-online-training.html
#Azure Data Engineer Training Ameerpet#Azure Data Engineer Training Hyderabad#Azure Data Engineer Online Training#Azure Data Engineer Course#Azure Data Engineer Training#Data Engineer Training Hyderabad#Data Engineer Course in Hyderabad
0 notes
Text
Adding a Column with Default Value to an Existing Table in SQL Server
To add a column with a default value to an existing table in SQL Server, you can use the ALTER TABLE statement combined with the ADD clause. The general syntax for adding a new column with a default value is as follows: ALTER TABLE TableName ADD ColumnName DataType DEFAULT DefaultValue; Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the syntax: ALTER TABLE TableName: This specifies that you’re modifying…
View On WordPress
#ALTER TABLE SQL Server#default value SQL#modify table SQL#SQL Server add column#SQL Server database management
0 notes